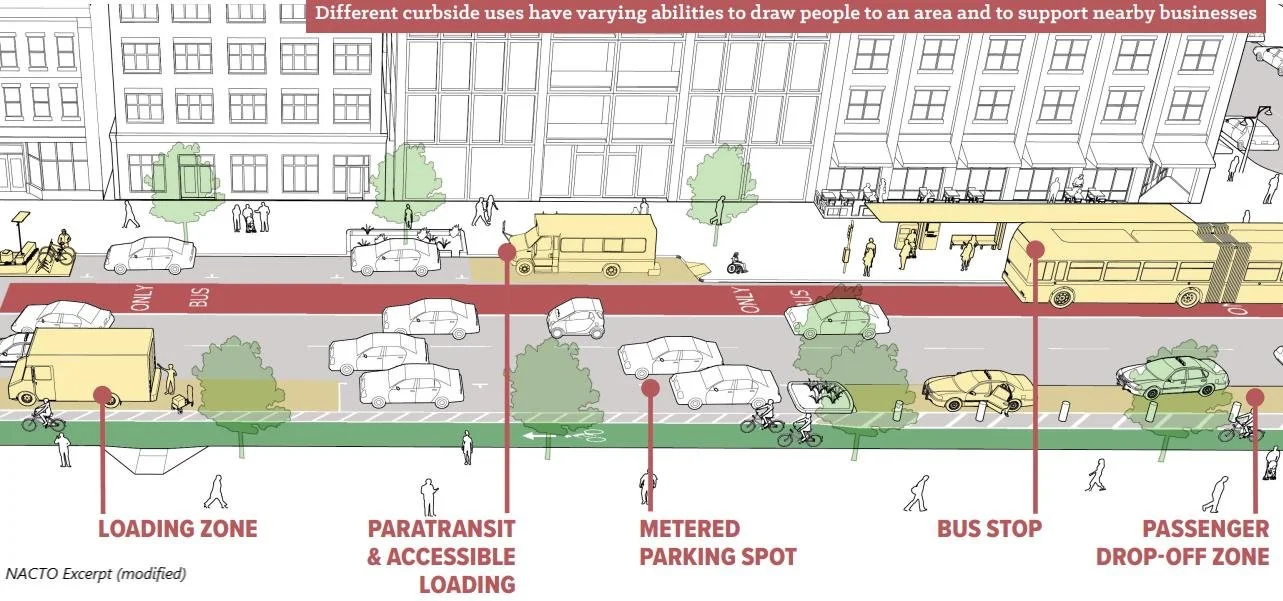
curbside management
Curbside management is the coordinated use of smart camera technology, dynamic curbside management tools, and parking occupancy detection/notification to optimize how curb space is allocated, monitored, and used for vehicles, deliveries, and public needs.
smart camera technology
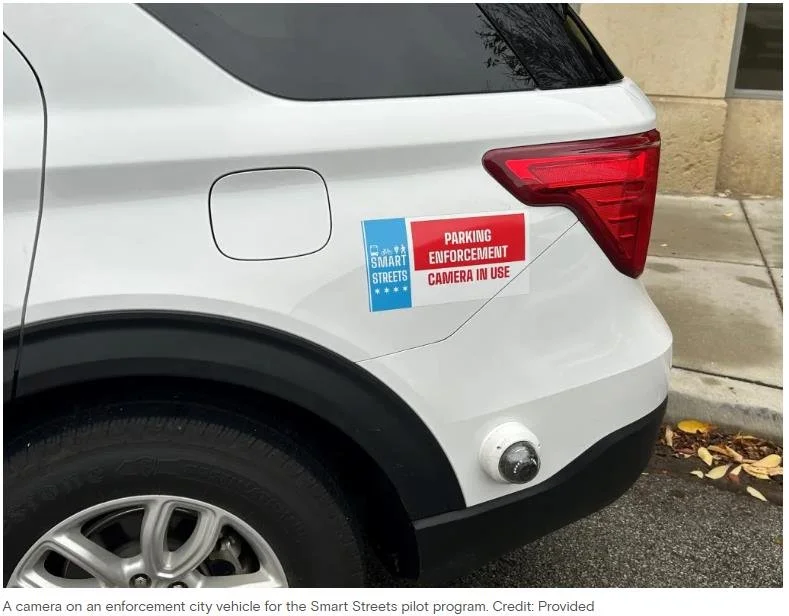
Camera Technology for Enforcement: Cameras are used to improve and automate the enforcement of parking and standing violations in bus and bike lanes.
Costs
Expenses vary based on the size, number, and type of camera installations. For example, Chicago’s pilot program on six buses cost $315,852, while the MTA’s system costs about $21,840 per system annually.
Key Considerations
Enforcement policies, such as whether violation tickets can be mailed
The specific focus of enforcement, like bike lanes, bus lanes, or both
Pros
Less traffic disruptions
Enhanced safety for cyclists & pedestrians
Better running buses and traffic flows
Cons
May require policy changes for ticketing
Privacy concerns
Hacking or internet connectivity issues
Representative Use Cases
Chicago DOT
Field Conditions
Best suited for busy, mixed-use areas like downtowns and central business districts (CBDs) that have protected bike and bus lanes.
dynamic curbside management
This technology uses data to help manage curb space efficiently, adjusting for different needs throughout the day.
Costs
Setting up the system can cost between $520,000 and $7.5 million, depending on how many loading zones are included (from 30 up to 500). There are also yearly fees starting around $56,000, based on the number of locations and cameras.
Key Considerations
Can violation tickets be mailed to drivers?
Who owns the poles where cameras will be installed?
Is power available at these locations, and who provides it?
How large the system will be and how many spots it will cover?
Pros
Revenues generated can be self-sustaining
Can minimize double parking
Improve freight movement
Cons
Better applied over numerous block faces
Policy/enforcement issues
Data management
Representative Use Cases – Currently in use across several cities like Pittsburgh and LA
Pittsburgh
LADOT
Field Conditions
Ideal for busy, mixed-use areas with high population density, such as downtowns and central business districts (CBDs).
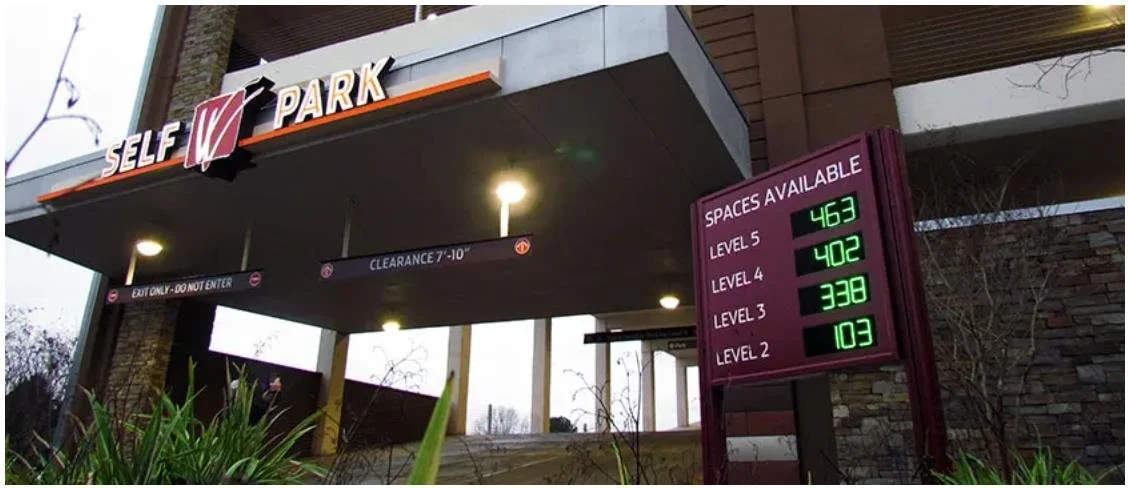
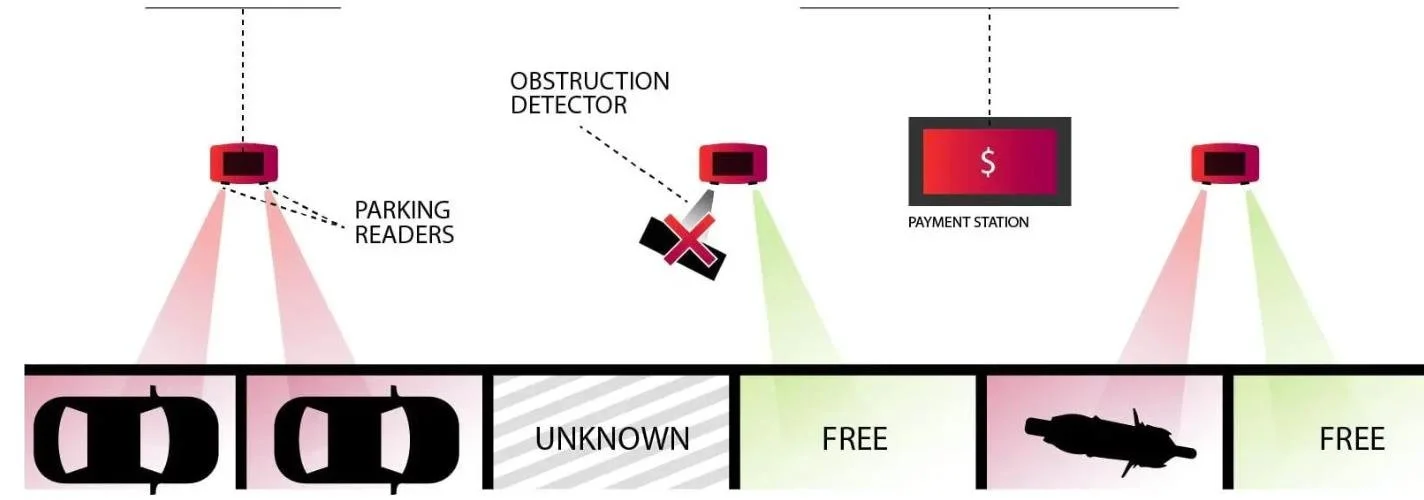
parking occupancy detection/notification
These systems make parking easier by providing real-time information about available spaces and guiding drivers to open spots.
Costs by Technology
Ultrasonic sensors: $300–$500 per parking space
Magnetometer sensors: Around $100 each
Smart parking meters: $250–$500 each
Basic AI-powered camera systems: $69 per camera per month
Full management systems: $30,000–$120,000
Key Considerations
Types of sensors or cameras used (inground or overhead)
Connectivity and how data is managed
Installation and ongoing maintenance costs
Whether the parking is on surface lots or in parking structures.
Pros
Reduced search and circulating time
Improved parking utilization
Reduced congestion
Cons
Sensor communication challenges
Sensor or camera obstructions
Accuracy