emerging technology
Emerging technology in transportation refers to innovations such as Connected Vehicles (CV), Automated Driving Systems (ADS), and Smart Pavement, which work together to enhance safety, efficiency, and real-time data sharing on roadways.
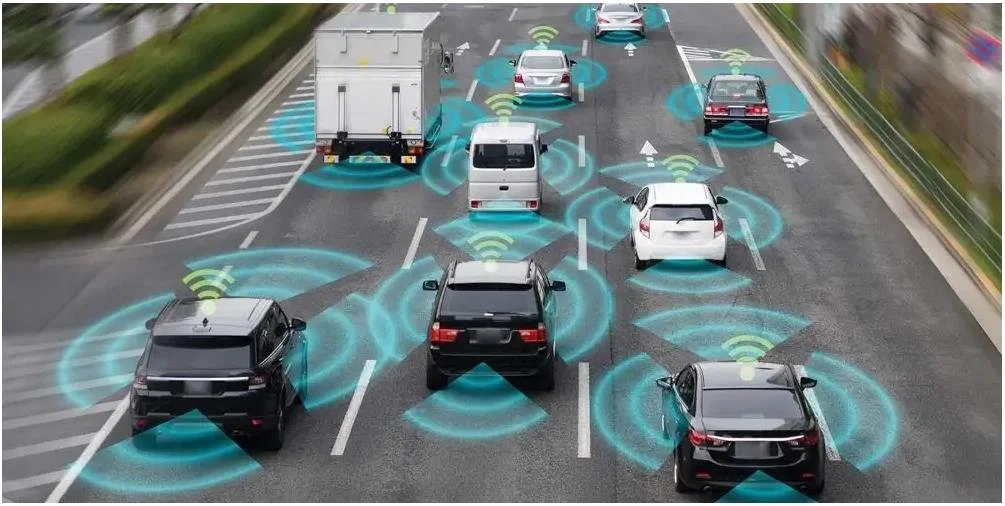
connected vehicles
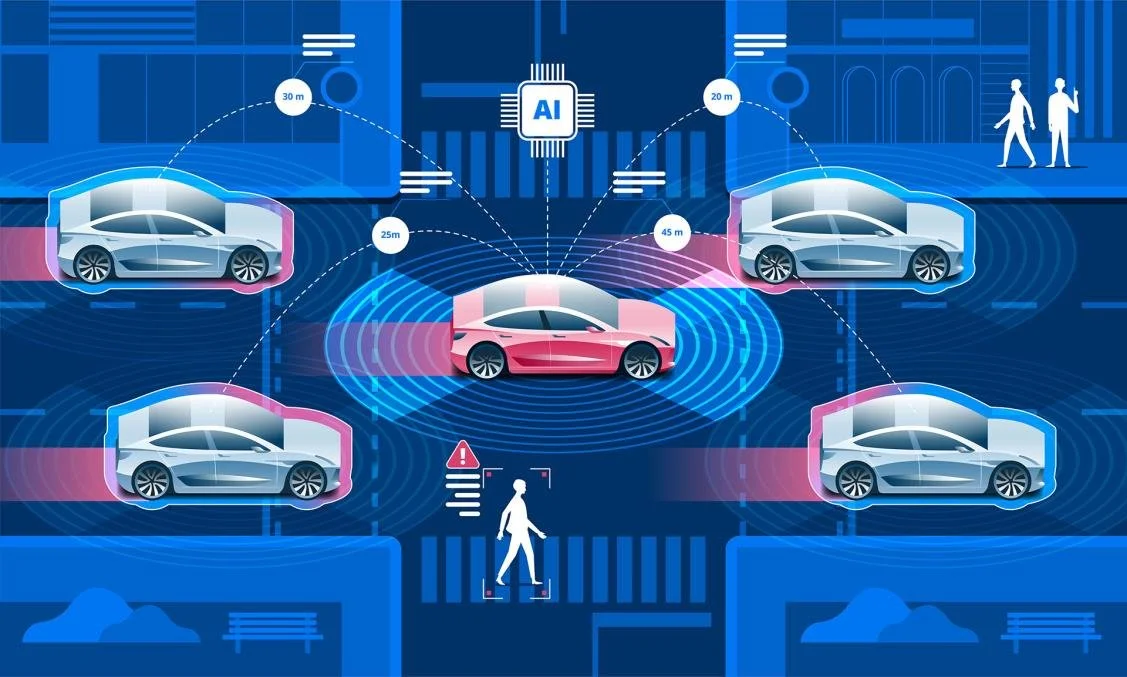
Connected vehicles are equipped to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and external systems through short-range wireless signals.
Costs
Adding connected vehicle technology to a car typically costs between $75 and $350, with subscription fees ranging from $8 to $35 per month.
Key Considerations
Regulations and legal frameworks
Integration with city and smart city systems
Protecting data privacy and security
Pros
Enhanced safety
Improved efficiency
Convenience
Cons
Network disruptions impact functionality
Cybersecurity risks/privacy concerns
Data misuse
Representative Use Cases
NYC CV Pilot Program
Wyoming I-80 CV Pilot
Field Conditions
Successful integration relies on close collaboration between automakers, city planners, and technology providers. A Wi-Fi network and digital infrastructure are needed.
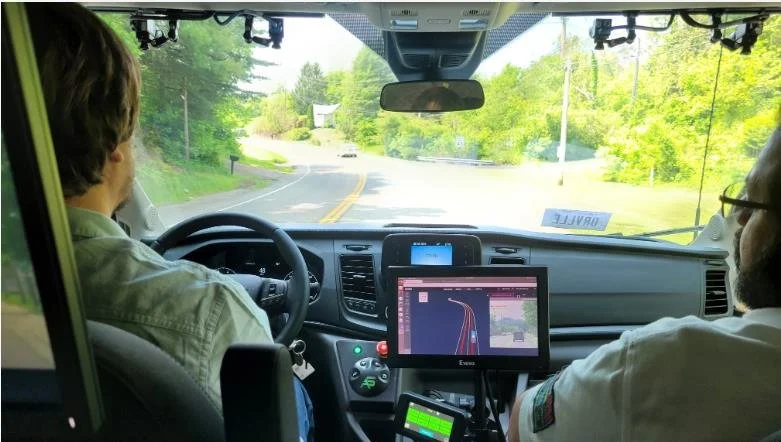
AUTOMATED DRIVING SYSTEM (ADS)
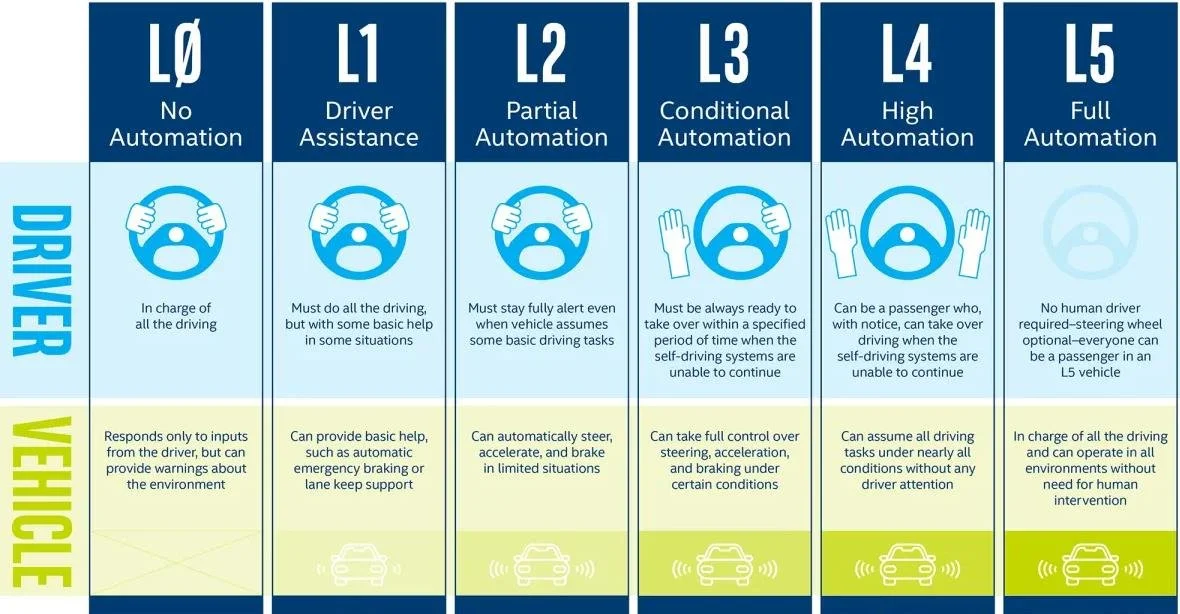
Also known as self-driving or autonomous vehicles, ADS use artificial intelligence, sensors, and mapping data to control vehicle movement and make decisions in real time.
Costs
Varies widely based on the level of autonomy and system complexity, ranging from $4,000 to over $200,000.
Key Considerations
Safety: Includes concerns around reliability, accident prevention, and protection from cyberattacks
Ethical: Questions about responsibility in the event of a crash
Legal Frameworks: Insurance requirements and how ADS vehicles operate in mixed traffic
Urban Planning: Potential impacts on road design, land use, and transportation systems
Pros
Efficiency in traffic
Accessibility
Reduced CO2 emissions
Cons
Cost
Mixed Traffic
Data requirements for vehicle communications
Representative Use Cases
Ohio
Field Conditions
Fully automated driving systems are best suited for highly controlled and integrated transportation networks where all vehicles and infrastructure are connected and communicating. Full deployment would require a reliable, high-precision system with widespread adoption of ADS technology across the entire network.
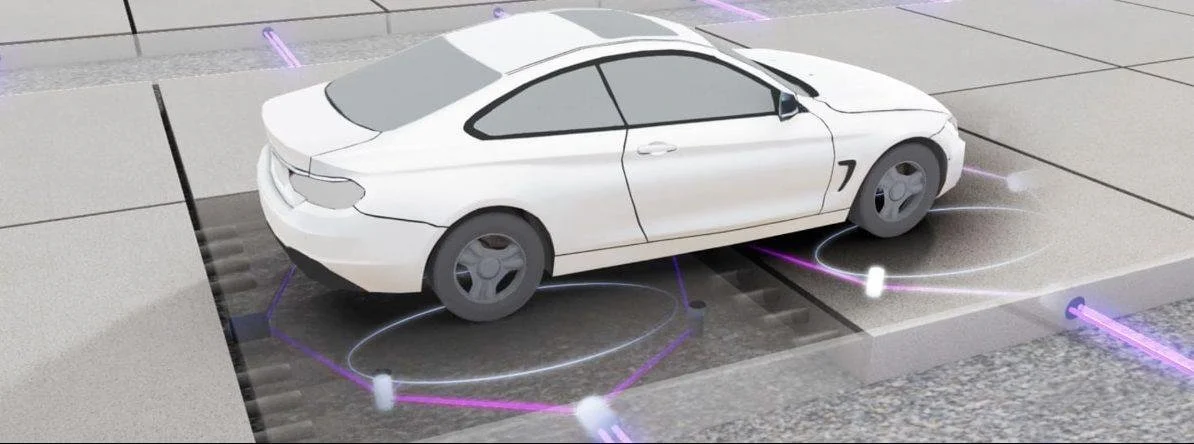
SMART PAVEMENT
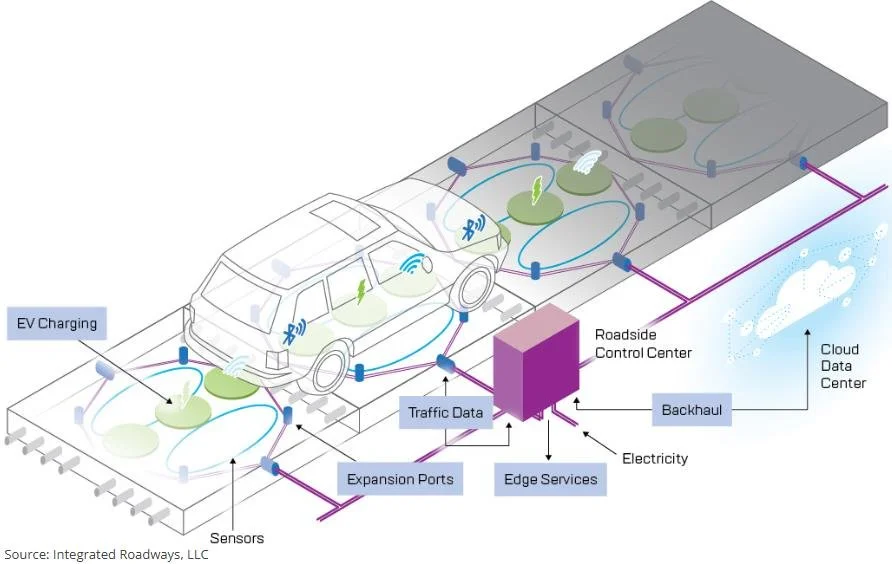
Roads equipped with sensors and advanced transportation technologies that monitor road conditions, manage traffic flow, and support features like wireless charging. This technology enables the pavement to communicate directly with data centers for real-time information.
Costs
Costs vary based on the technology used, averaging about $4 million per lane mile.
Key Considerations
High installation costs
Privacy concerns related to data collection
Durability and reliability of embedded sensors
Pros
Supports and facilitates other tech improvements (e.g. CVs, EV charging)
Modular and prefabricated
Cons
Data management and security
High cost