CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE
Charging infrastructure refers to the network of equipment, facilities, and systems needed to supply electric power to recharge electric vehicles including EV Charging Stations, Bicycle/Scooter Charging Stations and Bus Charging Stations.
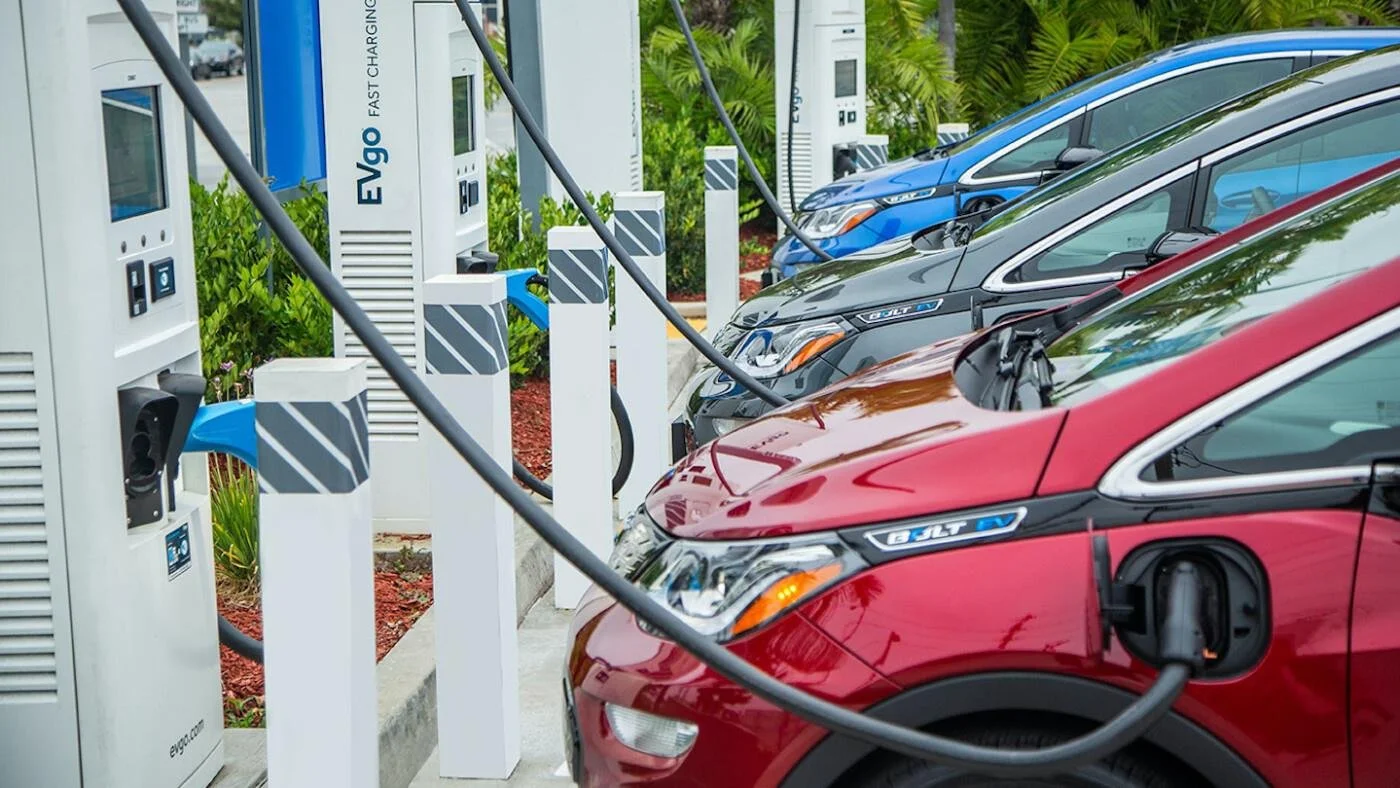
EV CHARGING STATIONS
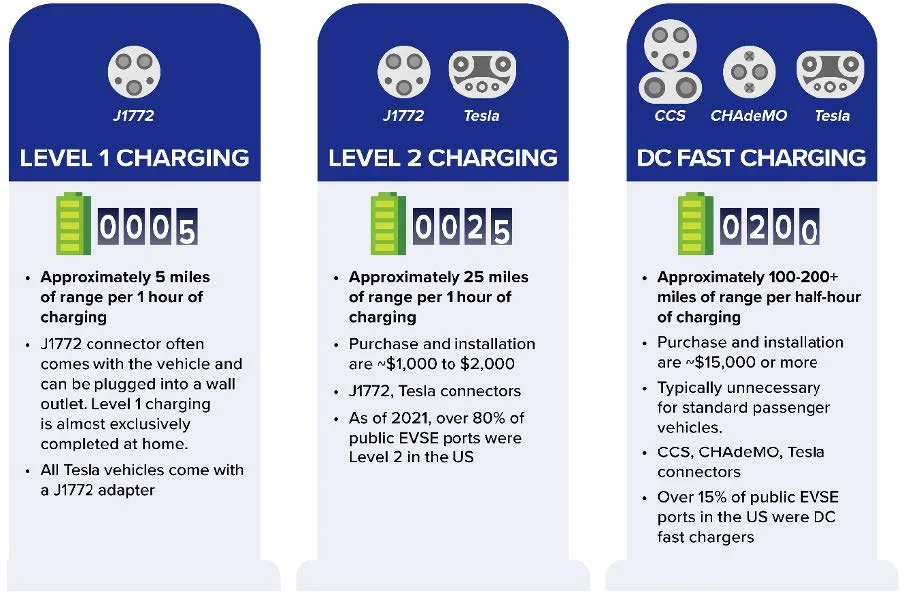
Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations deliver electricity to vehicles by connecting to the utility grid. These stations are typically categorized into three levels of charging. Additionally, inductive charging embedded in pavement offers a potential alternative method for powering EVs.
Costs
The cost of EV charging stations varies depending on several factors, ranging from around $3,000 for Level 1 chargers to over $50,000 for DC Fast Charging stations.
Considerations
Selecting the appropriate types of charging stations to install
Ensuring access to public utility connections
Evaluating overall costs
Determining the number of stations needed
Estimating how long vehicles will typically be parked at the location
Balancing proximity to activity centers with the need to avoid overloading capacity at signalized intersections
Pros
Lower emissions
Can be integrated into daily activities
Lower range anxiety
Cons
Time to charge
Power grid limitations
Maintenance costs
Representative Use Cases:
Ideal locations are areas with high density and a sufficient number of EV users to ensure consistent station usage.
Field Conditions:
Stations should be placed where they are convenient and likely to be used, but without obstructing traffic lanes whenever possible. Clear signage or digital information is needed to help EV drivers easily locate the stations.
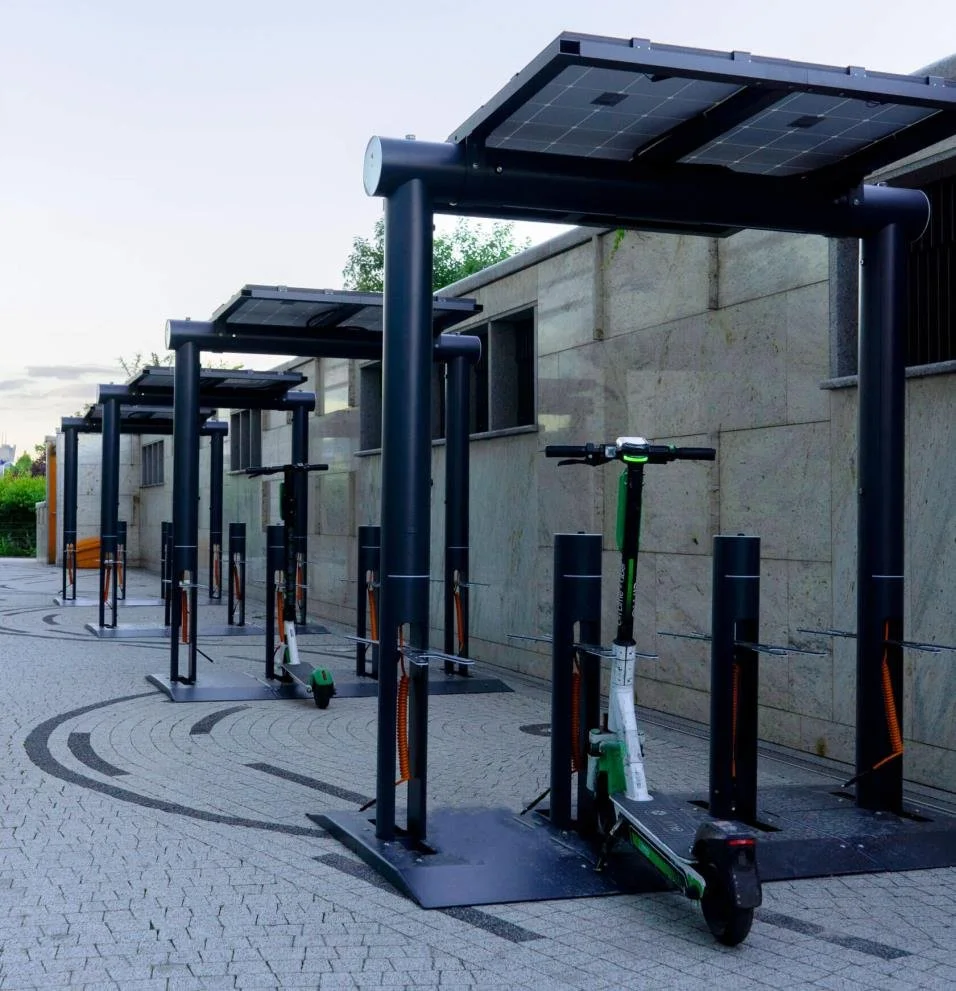
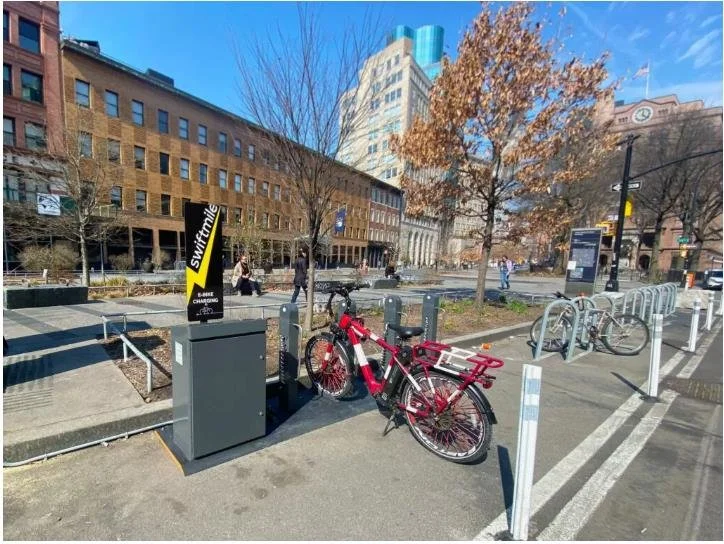
Bicycle/scooter charging stations
These are public or private charging points for electric scooters, bikes, and other small electric vehicles.
Costs
The price varies widely based on the type and complexity of the charging setup, ranging from $200 to $50,000.
Key Considerations
Visibility and pedestrian traffic for easy spotting
Convenience for users
Accessibility for all users
Proximity to other charging stations
Reliable power supply
Fire safety measures
Proper cable management to prevent hazard
Pros
Encourages alternate modes of transportation
Reduced range anxiety
Potential for smart city integration
Cons
May take-up limited sidewalk space
Cost and maintenance
Charging time
Representative Use Cases
NYC
Field Conditions:
Stations should be installed in locations where they will be actively used, while avoiding obstruction of sidewalks and pedestrian pathways. Clear signage or digital tools are needed to help users easily find and access these stations.
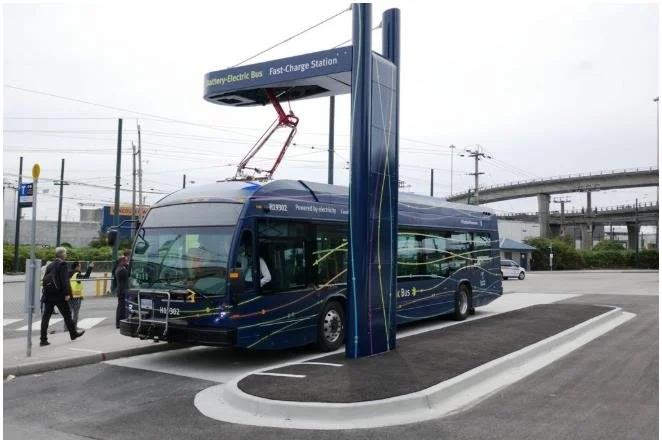
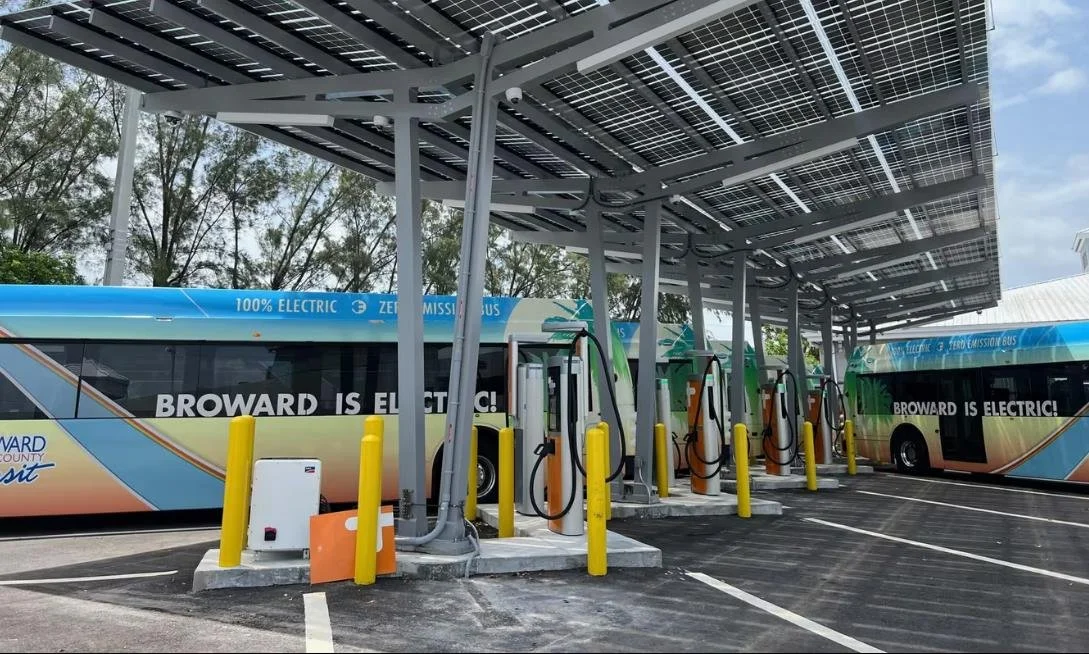
bus charging stations
Battery Electric Bus (BEB) Charging Facilities: These are specialized stations designed to provide electricity for recharging the batteries of battery electric buses (BEBs).
Costs
Typically ranges from $30,000 to over $150,000, depending on the number and type of chargers installed.
Key Considerations
Type and capacity of chargers
Availability and upgrades to electrical infrastructure
Strategic placement of charging locations
Total installation and maintenance costs
Potential for future system expansion
Pros
Environmental Benefits
Reductions in noise pollution
Cons
High Installation costs
Charging time